Ear infections are uncomfortable conditions typically arising due to inflammations caused by microorganisms.
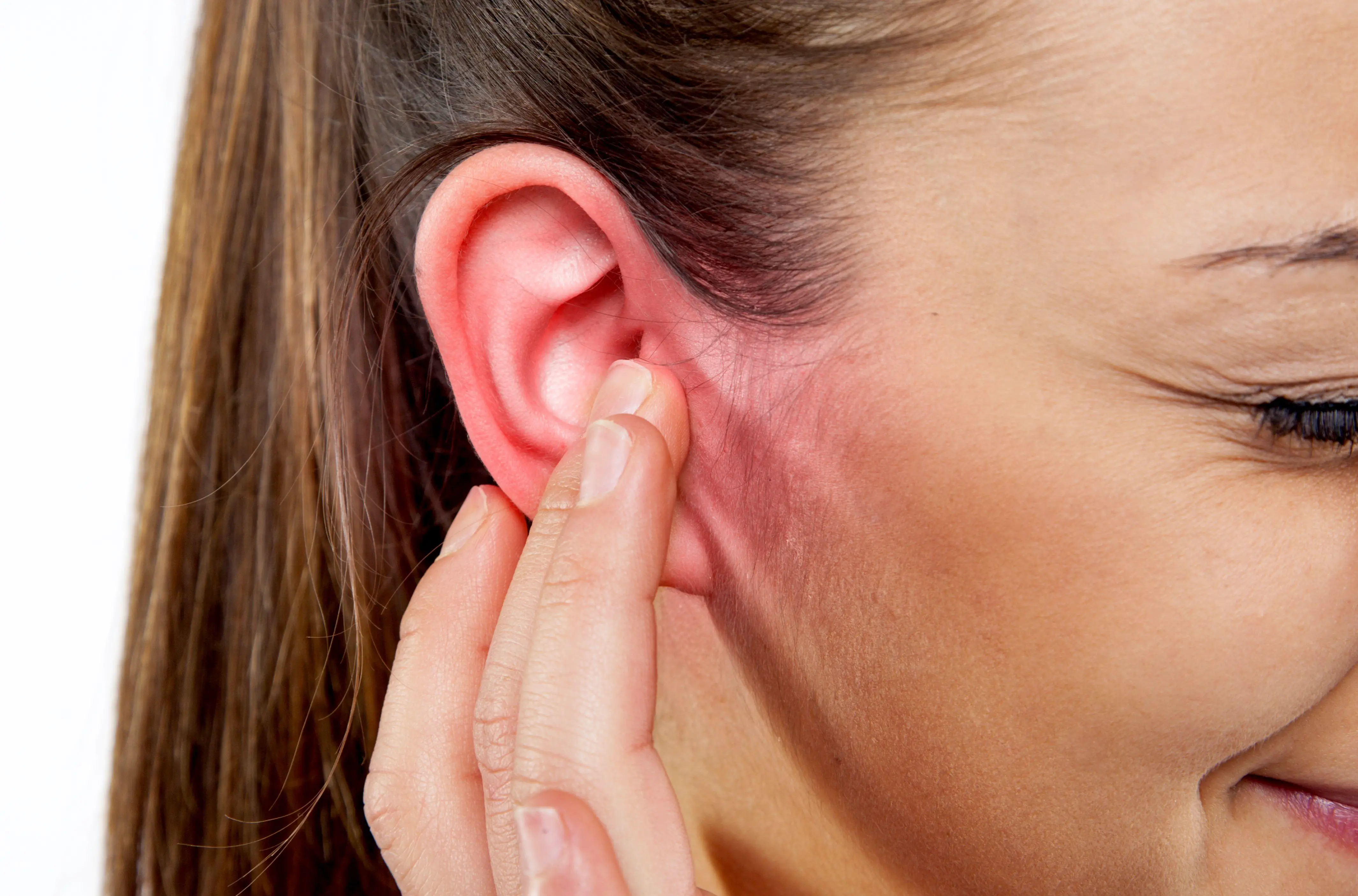
What Are Ear Infections? Ear infections are uncomfortable conditions typically arising due to inflammations caused by microorganisms. These infections can develop in different areas of the ear, and symptoms may vary depending on the type of infection. Types of Ear Infections Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Inflammations usually caused by bacteria or viruses. Common in children, it can lead to symptoms such as pain, hearing loss, and fever. Outer Ear Infections (Otitis Externa): Occurs due to the accumulation of earwax or prolonged presence of water in the ear. Symptoms may include itching, redness, and ear discharge. Inner Ear Infections: Typically caused by viral infections and can involve symptoms like balance issues, dizziness, and hearing loss. Causes and Risk Factors Microorganisms: Infections can occur when bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter the ear. Anatomical Predispositions: Anatomical features like enlarged adenoids, common in children, can increase the risk of infection. Weakened Immune System: A compromised immune system reduces resistance to infections. Symptoms and Diagnosis Symptoms vary depending on the type of infection: Middle Ear Infection: Pain, hearing loss, fever. Outer Ear Infection: Itching, redness, ear discharge. Inner Ear Infection: Dizziness, balance issues, hearing problems. Diagnosis involves a doctor conducting a physical examination of the ear and, if necessary, taking a culture of ear discharge. Treatment Methods Treatment varies depending on the type of infection: Middle Ear Infection: Use of antibiotics, pain relievers. Outer Ear Infection: Ear drops, anti-inflammatory medications. Inner Ear Infection: Rest, fluid intake, antiviral medications. Preventive Measures for Ear Infections Paying attention to ear hygiene. Drying ears after swimming. Strengthening the immune system against colds. These straightforward measures play a pivotal role in reducing the risk of ear infections. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is essential.
 TR
TR DE
DE RU
RU




